As a CPA who works closely with self-employed doctors and physicians, I’ve seen how overwhelming tax season can become.
When you are focused on patient care and running a medical practice, tracking expenses often falls behind. By the time it’s time to file, mixed business and personal spending, along with missed recurring costs can quietly reduce the savings you should be keeping.
My role is to help understand what 1099 tax rules are, which medical practice expenses are deductible and how to apply the right healthcare professional deductions without confusion or stress.
When you know what qualifies and keep your records organized, you should avoid overpaying and keep more of what you earn.
In this guide, I will walk you through the most important deductions for doctors to claim and show you how simple, consistent tracking can make tax season far easier and more predictable.
Understanding tax deductions for self-employed and physicians
When I talk to self-employed doctors and physicians about taxes, I always start with the basics. Tax deductions for self-employed doctors and physicians are simply business-related expenses that reduce taxable income under 1099 tax rules.
These are everyday costs required to run your medical practice. What the IRS considers ordinary and necessary.
In practical terms, medical practice expenses deductible can include rent, staff costs, insurance and deductible medical supplies you use to care for patients.
Let me explain with a scenario.
If you earn $80,000 and spend $20,000 on self employed doctor expenses like rent, equipment and insurance, you’re taxed only 60,000. That’s the power of physician tax deductions.
For 1099 self-employed doctors and physicians, tracking expenses properly ensures you maximize deductible medical supplies, home office deductions, and other healthcare professional deductions.
Top tax deductions for self-employed doctors and physicians under 1099 tax rules:
Here are some of the most common tax deductions for self-employed doctors and physicians every doctor should know about:
1. Medical supplies and equipment
Items like gloves, syringes, masks and stethoscopes are all considered deductible medical supplies.
Larger equipment, such as ECG machines or dental chairs, can also be written off gradually through depreciation. If it is something you use to treat patients, it likely qualifies as a business expense..
2. Professional liability (Malpractice) insurance
Every doctor needs malpractice coverage and the premiums you pay are fully deductible. It’s a necessary business expense that protects you from professional risks and legal claims.
3. Office rent and utilities
Rent for your clinic or chamber, along with electricity, water, phone and internet bills are valid deductions. If you work from home, you can claim a doctor home office deduction for the portion used exclusively for medical work.
4. Staff wages or contractor fees
If you are a small private practice owner with fewer than 5 employees and employ a receptionist, nurse or cleaner, their salaries are deductible. Payments to independent contractors, such as accountants or part time lab technicians, are also deductible, you just need to keep those receipts safe, and you are good to go.
5. Continuing medical education (CME)
Tax deductions are available for conference, workshop, online course, and even medical journal expenses. For example, you may be able to deduct both your registration and travel expenses if you attend training on innovative surgical methods.
6. Licensing fees and professional memberships
Renewing your medical license or paying annual fees to the association are considered ordinary and necessary business costs.
7. Technology and software
Tools like accounting software, online scheduling platforms, and electronic health record (EHR) systems are essential to modern operations. Because such items make your practice function more smoothly, the expense of buying or subscribing to them is deductible for healthcare professionals.
8. Vehicle and travel expenses
You deduct the mileage, if you drive to hospital, patient houses or any conferences. Even parking fees, cost related to car maintenance are deductible. Keeping a mileage log is essential to separate business use from personal use.
9. Marketing and advertising
Spending on your clinic’s website, running online ads or even printed flyers to attract new patients can be written off as medical practice expenses. Promotion helps to grow your business, making these costs legitimate deductions.
10.Health insurance premiums
Self-employed doctors and physicians can deduct the cost of their health insurance, including coverage for their spouse and dependents.
How to not miss out on tax deductions
1. Save all your receipts
Receipts are your backup.
They show exactly where your money went. Without them, the tax authority can reject a deduction, even if you truly spent the money.
Don’t ignore the small ones that $10 medical supply purchase or monthly software subscription adds up over a year.
Keep all the physical copies in a folder or take a picture of them and upload in a cloud app.
2. Separate personal and professional expenses
One of the most common mistakes I see self-employed doctors and physicians make is mixing business and personal spending.
I always tell my clients to use a separate bank account or credit card solely for their medical expenses.
This single step brings immediate clarity and saves you hours of stress.
3. Use a bookkeeping tool
If you are not a numbers person, let a software handle it for you.
A simple bookkeeping app like Tabby can automatically import your transactions, label them into categories such as rent, supplies, or travel and store digital copies of your receipts.
That means no more sorting through piles of papers or trying to remember what a $10 bill was a month ago. Automation keeps your finances organized year round and makes tax filling much smoother.
Common mistakes self-employed doctors and physicians should avoid
Over the years, I’ve noticed a few recurring mistakes that prevent self-employed doctors and physicians from fully benefiting from tax deductions for doctors. Avoiding these can make a significant difference in your tax outcome
1. Not claiming CME
One of the most common mistakes of self-employed doctors and physicians is to forget to claim for any programs or courses they enrolled to pursue further education. Document every paper related to CME to make sure you get full credit to your professional growth.
2. Forgetting smaller recurring costs
Monthly software subscriptions, regular supply orders might seem minor but over a year they can amount to a great deduction. Set a reminder to record every month so nothing slips through the cracks.
3. Mixing personal and medical expenses
Using the same account for personal and business expenses can create confusion and makes it harder to prove what’s deductible. Always keep your medical practice finances separate. It is cleaner, easier and much safer during audits.
4. Procrastinating until the last minute
Leaving everything for tax season is one of the biggest mistakes. Trying to organize a years’ worth of receipts in one weekend is a daunting task. Consistent tracking, even 10 minutes a week can help you to function in an organized way.
How Tabby can help self-employed doctors and physicians
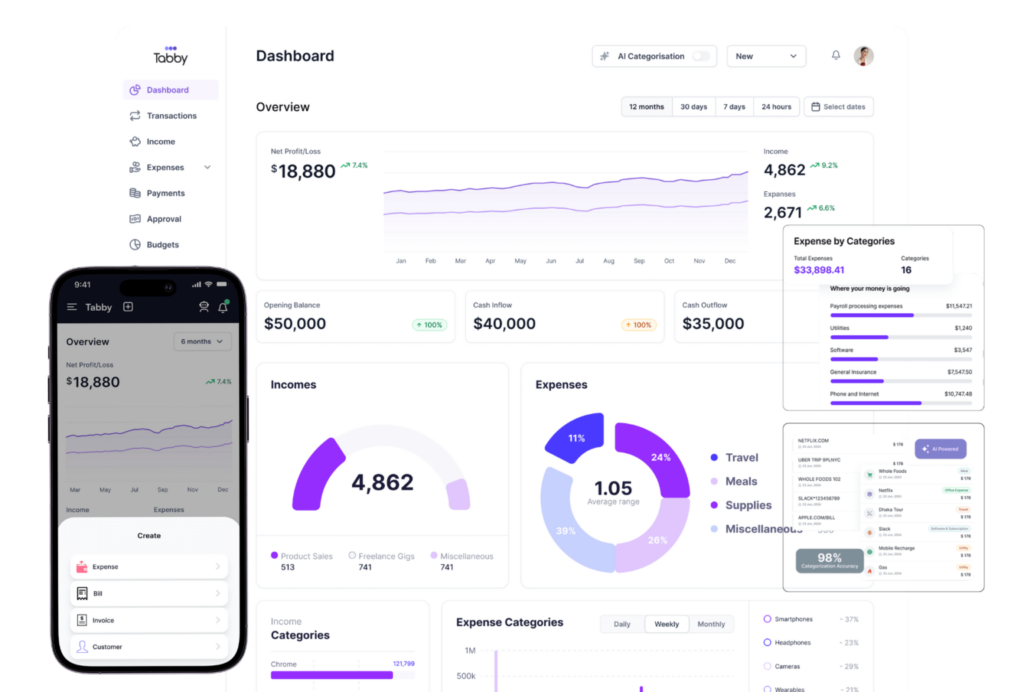
I have created Tabby to help self-employed professionals like you to easily handle your finances without spending hours.
Here’s how it helps to run things smoothly and simplify your bookkeeping and maximize your deductions.
1. Categorizes medical expenses automatically
Tabby’s AI-powered system automatically identifies and sorts your medical expenses into clear categories such as supplies, rent or utilities. You will always know where your money is going without having to enter your data manually.
2. Tracks malpractices insurance, CME and Office costs
Whether it’s your annual professional liability insurance, conference registration or recurring office bills, Tabby records these automatically. This means you will never miss a deductible cost, even those small ones that often go unnoticed.
3. Generates ready-to-file tax deduction reports
At tax time, Tabby compiles all your data into easy-to-ready reports that are ready to hand off to your accountant or upload directly to tax software.no spreadsheet, no guesswork. Just clear summaries of your deductible expenses.
4. Forever free plan for small practices
For self-employed doctors and physicians managing small clinics or starting out on their own, Tabby offers a Forever free plan for professionals with under $20,000 in annual expenses. It’s a cost-free way to stay organized and compliant all year long.
Bottom Line
Self-employed self-employed doctors and physicians and physicians already face a heavy tax burden, but there’s no reason to pay more than you legally owe.
In my work as a CPA, I’ve seen how a little organization and proactive planning can make a significant difference.
When you understand your deductions and track your expenses properly, you can claim every eligible write-off, lower your tax bill, and keep more of what you’ve earned.
My goal is to make sure you never overpay and that your finances truly reflect the work you put into your practice.
Tabby’s AI bookkeeping helps you to save money and time, it automatically tracks expenses, organizes receipts and prepares ready-to-file reports so nothing slips through the cracks.
Try Tabby for free and simplify tax deductions in this tax season so that you can focus on what truly matters: caring for your patients.
FAQS
- What expenses are deductible for self-employed doctors and physicians?
self-employed doctors and physicians can deduct ordinary and necessary expenses for running their practice. These are medical supplies, insurance, rent, utilities and software costs.
- Are continuing medical education costs deductible?
Yes, registration fees, textbooks, travel and courses that help you maintain or improve professional skills can all be deducted.
- Do self-employed doctors and physicians who work for themselves pay 1099 taxes?
Self-employed self-employed doctors and physicians pay taxes according to 1099 tax rules.
- Can self-employed doctors and physicians deduct health insurance premiums?
Absolutely, physician tax deductions include health insurance for you, your spouse and dependents.



